
Core Technologies in Smart Devices
Smart devices are electronic devices equipped with several communication technologies including Wi Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular technology, that link to other gadgets or networks. Automation is their ability to collect, evaluate, and share information by means of sensors, processing units, and communication interfaces. Core technologies in smart devices include smartphones, wristwatches, home automation systems, and industrial Internet of Things devices.
Evolution and development of smart technologies
From simple computing machines to sophisticated AI powered systems, smart technology has come a long way. Rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has enabled smooth interaction and communication between clever devices. Further driving their expansion are improvements in semiconductor technology, cloud computing, and wireless communication. These days, smart gadgets are used in healthcare, automotive industries, houses, and even smart cities to increase efficiency and quality of life.
Significance of Core Technologies in Smart Devices
Smart devices depend core technologies including sensors, microprocessors, artificial intelligence (AI), and embedded systems. These parts make possible flawless connectivity, enhanced security, real time monitoring, and automation. Knowing these tools well can improve device performance, security, and efficiency and also help to clear the road for next inventions.
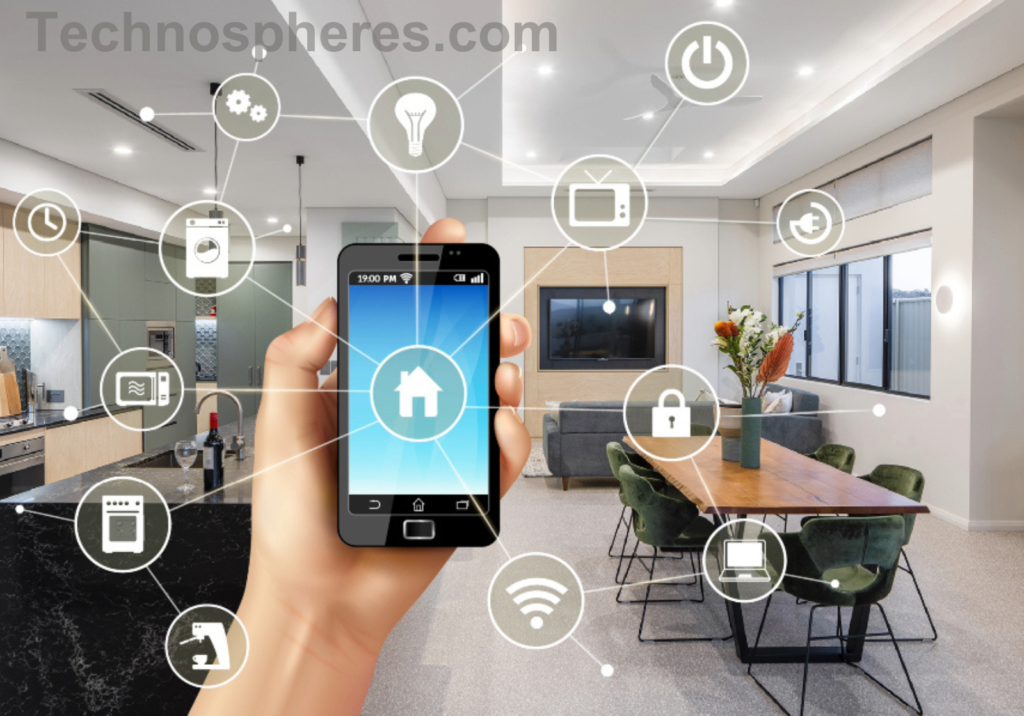

Sensors and Actuators
Smart devices depend on sensors to gather user and environmental information, so defining sensitive part of the devices. Physical inputs are converted by them into digital signals handled by the unit. Notable categories among
- Motion sensors (infrared sensors, gyroscopes, accelerometers): Found in smartphones, fitness trackers, gaming systems, and security devices to sense gestures, direction, and motion.
- Biometric Sensors (Fingerprint, Facial Recognition, Heart Rate Monitors): Used in security authentication, wearable health devices, and smart surveillance systems.
Used in smart parking systems and smartphones to deactivate screens during calls, proximity sensors. Light sensors: Change screen brightness in phones and operate wise lighting systems depending ambient light level. By converting electrical signals into mechanical motion, actuators let machines execute tasks. Examples are:
Motors:
• Found in automotive and industrial automation applications are pneumatic and hydraulic actuators.
• Medical instruments and precision engineering uses piezoelectric actuators.
Microprocessors:
The central unit of a computer system that manages data flow, executes calculations, and processes instructions is a microprocessor. It does not contain other peripheral elements within the same chip, input/output (I/O) ports, or memory. It depends rather on outside parts to operate correctly.
High Processing Power: Utilized in difficult computing operations including servers, personal computers, and high performance embedded systems. Suitable for uses demanding much processing power, multitasking abilities.
Differences between microcomputers and microprocessors
| Feature | Microprocessor | Microcontroller |
| Functionality | General-purpose CPU | Designed for specific tasks |
| Components | Requires external memory and I/O devices | Integrated CPU, RAM, and I/O ports |
| Applications | Computers, high-performance devices | IoT, embedded systems, automation |
Microcontrollers (MCU)
A microcontroller is a compact integrated circuit that includes a processor, memory (RAM & ROM), and I/O peripherals on a single chip. It is designed for specific embedded applications where dedicated control is needed.
Microcontrollers’ main characteristics are as follows:
- More compact and cost effective, All in One Design integrates memory, CPU, and I/O ports in one chip.
- Created for Particular Uses: Found in real time control applications in embedded systems.
- Power Efficient: Operates with minimal power consumption, suitable for battery powered devices.
- Optimized for control oriented systems instead of sophisticated calculations; slower processing speed than microprocessors.
Wireless communication technologies
Wi Fi, Bluetooth, and NFC.
- Wi-Fi: A high-speed internet connection is accessible for industrial Internet.
- Bluetooth: Facilitates communication between wearable devices, wireless headphones, and smart gadgets.
- NFC: Enables contactless transactions, keyless entry systems, and the transfer of information.

Cellular technologies (5G, 4G, 3G)
- Mobile data data and smart urban applications supported by 3G/4G LTE.
- 5G offers smart infrastructure low latency, very fast speed, and great IoT connectivity.
Z Wave, Zigbee, then LoRa on Internet of Things devices.
- Used in sensor networks and smart home automation are Zigbee and Z Wave.
- Long Range (LoRa): Enables smart agriculture and industrial monitoring with long distance, low power IoT connectivity.
Position of Embedded OS in Intelligent Products
Manages hardware resources and guarantees effective performance.
• Supports live current uses with little latency.
• Optimized code implies efficient processing and battery saving.
Popular Embedded OS
| Embedded OS | Applications |
| Android Things | Smart home devices, IoT systems |
| Free RTOS | Real-time control applications |
| Tiny OS | Wireless sensor networks |
Artificial Intelligence with Machine Learning
Foundation technologies in contemporary smart devices, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) enable them to analyze data, create intelligent decisions, and enhance user experience. Including consumer electronics, healthcare, automotive, and industrial automation, these tools improve efficiency, personalization, and automation for many fields.
1. Contribution of artificial intelligence as one of core technologies in smart devices
a) Decision Making and Automation
Smart devices use artificial intelligence and machine learning to run operations and take real time decisions without human intervention. For instance:
Smart thermostats automatically adjust room temperatures depending on user preference and learnt data.
AI powered voice assistants process natural language to give pertinent answers; Google Assistant might be mentioned.
Artificial intelligence helps self driving vehicles navigate securely, anticipate road conditions, and spot obstructions
b) Personalization and Adaptive Learning
- Smart gadgets can use machine learning algorithms to study user behavior and then customize experiences as needed.
- Smartphones use artificial intelligence to suggest applications, maximize battery life, and improve photography.
- Specially based on viewing history, smart TVs and streaming services offer content ideas.
- Wearable devices follow fitness data and recommend tailored exercise programs.
c) Better Security and Privacy features
- By letting, artificial intelligence reinforces the safety of intelligent devices:
- For safe verification using smartphones and smart locks, use facial recognition.
- Cybersecurity anomaly detection helps in the identification of real time menaces.
- AI based banking and financial transaction fraud detection systems.
d) natural language processing (NLP) and voice recognition
- NLP allows clever gadgets to react to voice instructions, thus transforming human device contact.
- Voice instructions are processed and Internet of Things devices are managed by smart speakers (e.g., Amazon Echo, Google Nest).
- Artificial Intelligent chatbots and virtual assistant support customer services.
2. Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies present in smart devices
a) Edge Processing and On Device Artificial Intelligence
- Rather than depending only on cloud processing, on device AI models are now more and more used.
- Less data use, quicker response times, more confidentiality
- AI driven cameras process video feeds locally without transmitting data to outside servers.
b) Deep Learning vs. Machine Vision
- Smart devices support speech and image recognition thanks to deep learning.
- AI driven security cameras spot unauthorized activity.
c) Wise Adaptation through Reinforcement Training
- Smart devices use reinforcement learning to increase over time by learning from their interactions.
- Self driving vehicles maximize navigation by considering actual events.
Issues and Factors to Consider
- Smart devices run by artificial intelligence gather great quantities of user data, thereby worrying privacy experts.
- Decentralized processing and secure data encryption (e.g., federated learning) go a long way in solving these problems.
- Resource intensive AI computations might degrade battery life in mobile gadgets.
- Helping to maximize performance are energy efficient AI chips like Google’s Tensor Processing Units (TPU) and Apple’s Neural Engine.
- Models based on AI can make unjust or incorrect judgments stemming from training data biases.
Edge Computing and Cloud Computing as one of core technologies in smart devices
Core technologies underpinning intelligent devices, which can therefore process, store, and analyze data effectively, are edge computing and cloud computing. Smart devices—from cellphones and IoT devices to self driving cars and industrial sensors—depend on each technology to improve their capacities.

Instead of selecting one over the other, several clever gadgets follow a mix approach:
- Edge computing deals with slow latency, real time work (e.g., mobile phone facial recognition).
- Cloud computing handles sophisticated algorithms, massive data analytics, and artificial intelligence model training.
- A good security camera could, for instance, analyze motion locally using edge computing while transmitting saved video to the cloud for long term storage and study.
Battery Technology and Power Management
- ARM based processors that have ultralow power modes save power.
- Dynamic voltage scaling and effective task scheduling are some energy saving methods.
- Smart wearables using inductive charging, solar energy, and kinetic energy harvesting.
Security and Confidentiality Techniques
- Using AES, RSA encryption guarantee secure data storage and communication.
- Device security using face recognition and fingerprint scanners.
- Security measures based on hardware to deter unauthorized access.
Applications of Core Technologies in Smart Devices
Core technologies such the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Big Data, and Cloud Computing are changing numerous industries by letting appliances to be smarter and more efficient. These tools have multiple significant applications in many disciplines.
Everyday Life Illustrations
- Smart homes use many linked gadgets and automation systems to improve energy efficiency, safety, and comfort.
- Smart thermostats (e.g. Nest, Ecobee) will lower room temperatures based on occupancy patterns and user wishes.
- Smart Lighting (Philips Hue, LIFX): Automatically turn on/off using voice commands or motion detection.
- Smart doorbells and cameras enable real time checking and warnings—which can be found in many security systems including Ring and Arlo.
- Voice controlled, AI driven assistants make daily tasks easier.
- Google Assistant, Siri, Amazon Alexa: Assistance with online shopping, smart device management, weather forecast, and reminders.
- Found in productivity software and customer support for improved user contact, chatbots & apps run on artificial intelligence.
Industrial Uses
- Smart technologies help businesses to raise operations, lower costs, and increase efficiency.
- Smart factories enabled by IoT: Machines communicate to spot issues and avoid failures.
- RPA: AI driven robots engage in repetitive actions, therefore lowering mistakes and human labor.
- Sensors gather data to forecast equipment breakdowns before they occur, therefore reducing downtime.
Agriculture uses.
- Farmers are using intelligent gadgets to keep track of and perfect agriculture operations.
- Use drones and GPS Sensors to track plant growth, soil moisture, and crop health.
- By catching insects early and using precision treatment, AI driven pest control would help to cut down on pesticide use.
- Modern agriculture depends greatly on wise use of water and effective irrigation techniques.
- Automated Irrigation Systems: Control the water supply with sensors measuring soil humidity.
- Using IoT based weather monitoring, it forecasts rainfall and as required modifies irrigation plans.
Medical and Healthcare Uses
- Smart devices help users track their health metrics in real time.
- Smartwatches & Fitness Bands (e.g., Apple Watch, Fitbit): Monitor heart rate, oxygen levels, and physical activity.
- ECG and Blood Pressure Monitors: Provide early warnings of potential heart conditions.
- Remote surveillance and telemedicine
- Smart medical tools improve the efficiency of and access to healthcare.
- Aid patients in controlling long term illnesses like diabetes using IoT enabled health tracking (e.g. glucose monitors, smart tablet dispensers).
- Machine learning algorithms search medical records to find early symptoms of illnesses.
Future view on Essential Core Technologies in Smart Devices
The ongoing development of these fundamental technologies is defining the future of smart devices, therefore rendering them more intelligent, flexible, and efficient. Smart appliances will be even more everyday embedded as breakthroughs like AI driven automation, ultrafast 6G networks, and improved security solutions appear. Still, issues including data privacy, energy use, and interoperability have to be solved for technology to grow securely and sustainably.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Smart devices are said to be further entwined with artificial intelligence and machine learning, therefore improving their ability to learn from user actions and adjust correspondingly. AI driven edge computing will lower latency and enhance real time processing, hence letting devices to operate independently of cloud computing more effectively.

Internet of Things (IoT) and Connectivity Improvements
Increasingly interwoven network of smart devices will result from the explosion of IoT. Growing communication standards including 5G Advanced, Wi Fi 7, and possibly even 6G in the future will improve the speed, dependability, and efficiency of these gadgets. Improved connectivity will benefit industrial IoT (Iiot), smart cities, and smart homes, leading to smooth communication among many devices.
Integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR)
Future smart devices will depend on better sensors and real time processing to run more immersive AR and VR programs. Especially in domains including gaming, health, education, and remote work collaboration, AR smart glasses, mixed reality headsets, and smart contact lenses are predicted to totally transform user interaction with the digital world.
Advanced Sensor Technology and Edge AI
Sensors of the next generation with improved accuracy and sensitivity will be integrated into smart products that allow for better environmental awareness. Thanks to on device (edge AI) artificial intelligence processing, biometrics, health monitoring, motion recognition, and real time analytics will be run, thus lowering data transfer requirements and improving security.
Quantum computing and intelligent devices.
Quantum computing, though still in its infancy, could revolutionize smart devices by permitting very fast processing of sophisticated AI models. In areas including cryptography, optimization, and data analysis, this could be especially helpful.
Energy saving technology parties
Smart devices face significant obstacles in power usage and battery life. Solid state batteries, energy harvesting technologies like solar and kinetic energy, and AI driven power management to maximize energy efficiency will be future trends. Furthermore, to lower waste, item production will more and more depend on biodegradable and recycling materials.
Security and data privacy via blockchain
Security fears are on the rise as intelligent devices compile and analyze huge quantities of user data. Decentralized data storage, secure transactions, and improved cybersecurity all depend on blockchain technology. Encrypted, tamperproof ledgers will protect internet of things systems and stop data breaches.
Improving the human machine interface (HMI)
Future intelligent devices will stretch the limits of human machine interaction. Brain computer interfaces, speech identification, and gesture controls innovations will provide more natural interactions with technology. With little input, devices will offer a smooth experience by predicting user demands.
Robotics and automation in small devices
More prevalent will be artificial intelligence guided automation devices, independent drones, and robotic assistants. Self cleaning systems, home security robots, and artificial intelligence driven personal assistants will enable smart home devices to offer robotic performance handling complex tasks independently.
Display technologies flexible and adaptable.
The development of flexible, rollable, and even polished displays will alter the shape of intelligent devices. Therefore, modern developments in Micro LEDs and OLED will produce devices that are creatively stunning as well as more energy efficient, thus paving the way for next generation items including foldable smartwatches and augmented reality displays embedded into daily usage objects.
Conclusion
Intelligence, connectivity, and automation have been seamlessly incorporated into our daily lives by smart devices, therefore changing our technology interaction. Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), wireless communication protocols, edge computing, sensors, and security mechanisms represent some of the core technologies behind these gadgets. Improving the performance, effectiveness, and consumer experience of smart gadgets depends upon all of these.
Smart devices can react in real time, customize user experience, and handle data intelligently thanks to artificial intelligence and machine learning. Devices can connect seamlessly using IoT to create big ecosystems that enhance home, industry, and medical automation. Fast and dependable data transfer is made possible by wireless communication systems such Wi Fi, Bluetooth, and 5G, whereas edge computing improves performance by handling data near to the source rather than relying on cloud infrastructure.
read more about Tech News from Technospheres.


Smart devices have indeed revolutionized the way we interact with technology, making everyday tasks more efficient and intuitive. The integration of sensors, AI, and connectivity has brought about a new era of automation and convenience. However, I wonder if there’s a risk of over-reliance on these devices, especially in critical areas like healthcare and automotive industries. How do we ensure that the security of these smart systems is robust enough to prevent potential breaches or failures? Additionally, while the advancements in IoT and cloud computing are impressive, are we considering the environmental impact of such widespread technology use? It’s fascinating to see how smart devices are shaping the future, but I’m curious—what’s the next big leap in this field? Could quantum computing be the game-changer for smart technology?