
Big Data and the Ethics of Cybersecurity
In our digital age, data has become a top asset. Big data and the ethics of cybersecurity explore privacy, security, and ethical challenges in data protection and innovation. Because growth in big data and ethics of cybersecurity have kicked off key talks, companies and people churn out loads of info. Quick advances in AI, machine learning, and data crunching have boosted our power to handle data. Yet, these steps forward also bring big ethical and security hurdles we need to tackle head-on.
Big data analytics helps companies make smart choices, boost customer satisfaction, and work more . But when it comes to handling sensitive info ethical issues pop up parking talks about privacy, keeping data safe, and ethical hacking. At the same time, cybersecurity plans need to change to protect all this data from online threats. This article digs into how big data and cybersecurity connect focusing on ethical concerns, rules and regulations, and the best ways to handle things.
Understanding Big Data
Big data refers to the large volumes of structured and unstructured data that are generated at high velocity. Moreover, these data sets are difficult to process using traditional data management tools. So the characteristics of big data are commonly known as the three Vs:
- Volume – The amount of data generated is vast, often in petabytes or exabytes.
- Velocity – Data is generated in real-time or near real-time from various sources such as social media, sensors, and transactions.
- Variety – Data comes in different formats, including text, images, videos, and structured databases.
Big Data refers to vast amounts of structured and unstructured data generated at high speed from various sources. It is processed using advanced analytics and AI to extract valuable insights.
Uses of Big Data
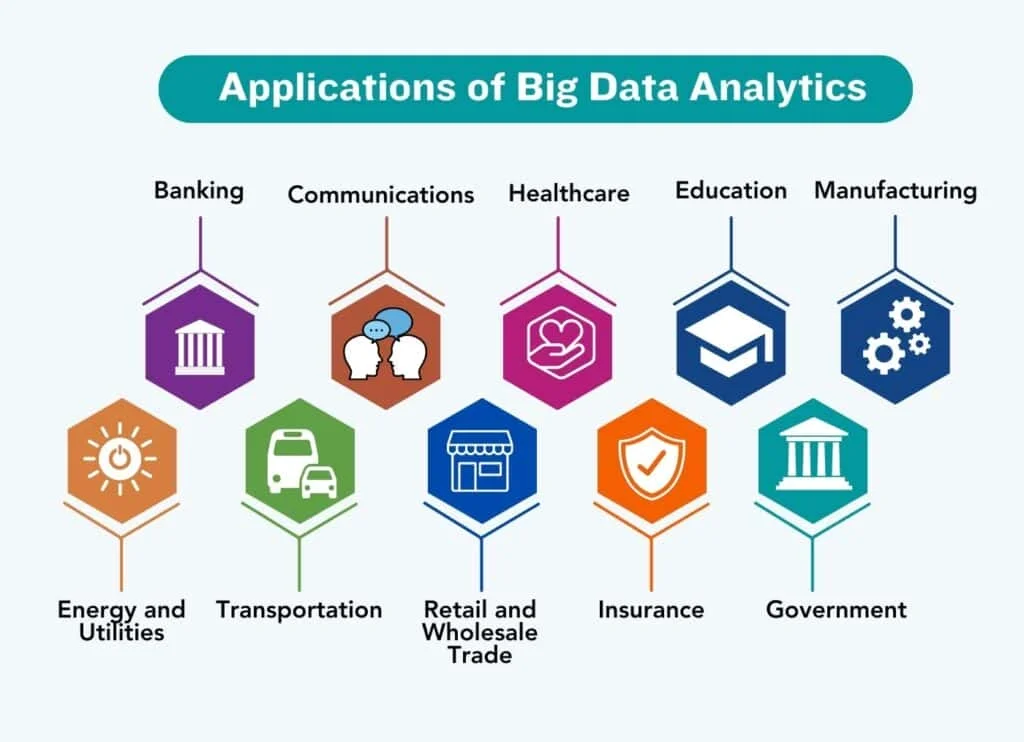
Business Analytics & Decision-Making
- Helps companies analyze consumer behavior and trends.
- Improves strategic planning and operational efficiency.
Healthcare & Medicine
- Enhances disease prediction and personalized treatment.
- Supports medical research and drug discovery.
Finance & Banking
- Detects fraud and prevents cybercrime.
- Helps in risk assessment and investment predictions.
Retail & E-commerce
- Personalizes customer experiences and targeted marketing.
- Optimizes inventory management and pricing strategies.
Manufacturing & Supply Chain
- Predicts equipment failures and enables predictive maintenance.
- Optimizes logistics and supply chain management.
Social Media & Marketing
- Analyzes user interactions for targeted advertising.
- Enhances brand reputation management.
Education
- Tracks student performance for personalized learning.
- Helps institutions in resource management and curriculum development.
Smart Cities & IoT
- Improves urban planning and traffic management.
- Enhances energy efficiency and sustainability.
Security & Law Enforcement
- Helps in crime prevention through data analysis.
- Strengthens cybersecurity measures.
Environmental Monitoring
- Analyzes climate change patterns.
- Supports disaster prediction and response.
The Value of Big Data
- Data-Driven Choices – Helps businesses and governments to create strategies based on facts.
- Better Productivity – Streamlines work and cuts expenses.
- Happier Customers – Offers tailored interactions and support.
- Spotting Scams & Managing Risks – Stops money and security threats.
- New Ideas & Staying Ahead – Pushes tech progress and market dominance.
- Seeing the Future – Aids in guessing trends and what’s to come.
- Growing Bigger – Backs companies to expand their work .
Concerns regarding Big Data and the Ethics of Cybersecurity
The rise of big data and the ethics of cybersecurity has led to numerous ethical dilemmas. Some of the primary ethical concerns include:
Ethical Worries Linked to Big Data Privacy
Privacy stands out as a key ethical concern in the realm of big data. Hence, Companies gather huge amounts of personal information often without people’s clear approval. This brings up questions about data ownership and proper usage.
| Concern | Description |
| Data Ownership | Users often do not own the data they generate, leading to concerns about misuse. |
| Informed Consent | Many users are unaware of how their data is collected, stored, and shared. |
| Data Anonymization | Even anonymized data can sometimes be de-anonymized, leading to privacy breaches. |
Unfairness and Discrimination
Big data analysis can reinforce present prejudices leading to discriminatory treatment in employment, loans, policing, and so forth. If the information used to train AI is biased, the decisions of AI might also be biased harming minority populations more than anyone else.
Surveillance and Government Overreach
Big data affects the way governments and businesses monitor individuals, which raises concerns about our liberties. Individuals cannot often visualize how big data collection schemes operate and therefore debate whether they are legal or ethical.
Cybersecurity Issues in Big Data
With increasing big data, the cyber threats rise as well. So organizations are challenged to protect huge amounts of confidential information from cybercriminals. A few significant issues are:
Unauthorized Access and Data Breaches
Cyber attackers attack major data stores with huge Data Breaches. As a result ineffective security controls make sensitive corporate and personal information accessible, resulting in identity theft, financial fraud, and reputations loss.
Important Cybersecurity Challenges in Big Data
| Threat | Description |
| Data Breaches | Unauthorized access leading to theft or leakage of sensitive data. |
| Malware and Ransomware | Malicious software that encrypts or steals data, demanding ransom for access. |
| Phishing Attacks | Cybercriminals use deceptive emails or messages to steal personal information. |
| Insider Threats | Employees or partners with access to data misuse it for personal or malicious reasons. |
Protecting Cloud-Based Data
Since most businesses already make use of cloud computing, ensuring robust security controls for cloud data is the key. Ineffective cloud security configurations could leave data exposed to cybercriminals.
Ethical Hacking and White Hat Security
To combat cyber attacks, ethical hacking is necessary. Organizations hire ethical hackers (white hat hackers) to find and repair bugs prior to the same being taken advantage of by malicious hackers. However, ethical concerns arise regarding how much ethical hacking must be allowed and regulated.
Ethical Issues in Cybersecurity
Keeping cybersecurity practice moral is as critical as information security. Moral practice of cybersecurity has the belief that security works for the protection of the rights of people while effectively combating cyber attack.
Ethical Practice of Data Gathering
Organizations must ensure ethical practice in the collection of data, e.g., obtaining knowledgeable consent and making it clear the way data shall be utilized.
Security vs. Privacy
Achieving balance between robust cybersecurity and protection of data privacy is the trick. Extremely strict controls can undermine liberty, but inadequate security threatens information.
Adherence to Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Businesses must comply with data privacy acts, which are:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – The European Union has data privacy in place.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) – Provides the citizens of California privacy rights.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) – Protects healthcare-related information within the United States.
Key Regulations Governing Big Data and Cybersecurity
| Regulation | Description |
| GDPR | Protects the personal data and privacy of EU citizens. |
| CCPA | Grants California resident greater control over their personal data. |
| HIPAA | Sets standards for protecting sensitive patient health information. |
| SOC 2 | Ensures organizations securely manage data to protect customer interests. |
Best Practices for Ethical Cybersecurity in Big Data

- Use Strong Encryption – Data will be kept out of reach from unauthorized parties through encryption.
- Regular Security Audits – Regular audits identify vulnerabilities before cyberthieves can exploit them.
- Transparent Data Policies – Businesses must be open about gathering, storing, and using data.
- Invest in Cybersecurity Training – To put it more simply, staff must be trained in security protocols to avoid unintentional breaches.
- Use AI and Machine Learning for Security – AI-powered security can potentially identify and respond to threats in real-time
The Future Outlook of Big Data and the Ethics of Cybersecurity
The future of big data and the ethics of cybersecurity is likely to transform industries, governments, and human interactions. So with increasing data generation, new technologies will come into existence to process, analyze, and gain insights from huge datasets. The following are the major areas defining the future of Big Data:
Evolution in AI and Machine Learning
Big Data will more and more rely on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to deliver significant pattern extraction. So self-improving algorithms will be used to make real-time decisions, forecast, automate functions in healthcare, finance, and smart cities, among others. AI-powered data analysis will continue to evolve with regards to its sophistication, involving less human interference but more precision and efficiency.
Quantum Computing’s Impact on Big Data
Quantum computing will transform Big Data analysis with the ability to process enormous data sets at unheard-of speeds. As a result, this will support intricate simulations, improved cryptographic security, and improved predictive modeling across climate change projections, personalized medicine, and risk assessment in finance.
Data Monetization and Economy
Data will become the biggest economic resource, and data-driven business models will thrive. Companies will provide customer data more readily for better marketing, customer experience, and revenue generation. Additionally, data ownership and privacy ethical dilemmas will become a significant issue with companies weighing consumer trust against regulation.
IoT Integration and Edge Computing
The spread of Internet of Things (IoT) devices is going to result in distributed data processing via edge computing. Data will be processed not via the cloud but locally, reducing latency and enhancing security. Edge computing will be the basis for smart cities, self-driving cars, and real-time industrial automation decision-making.
Tightened Controls and Data Processing
Governments and regulators will introduce tighter data control regulations to protect customer data. Moreover, GDPR and subsequent data sovereignty regulations will define how organizations will deal with data collection, storage, and processing. Organizations will have to give priority to ethical data management to comply with these new regulations.
The Future of big data and the ethics of cybersecurity security vulnerabilities also increase, and with them come profound questions of ethics. Future cybersecurity will not just be data security but also equality, privacy, and trust on the internet.
Key future trends in cybersecurity ethics include:
Ethical AI in Cybersecurity
AI-powered cybersecurity solutions will be the norm, pre-empting and blocking attacks in real-time. But biased AI algorithms, automated monitoring, and AI in cyberattacks as an instrument of abuse will all need to be tackled. Organizations will have to implement open AI ethics policies so that bias and prejudice are excluded from security solutions.
Enhanced Privacy Protections and Digital Rights
With rising concerns over mass surveillance and data breaches, the future will see stronger privacy-preserving technologies, such as zero-knowledge proofs, homomorphic encryption, and decentralized identity management. Individuals will gain more control over their data through blockchain-based identity systems and privacy-enhancing technologies.
Balancing Business Growth with Ethics and Privacy
Data will be the most precious economic asset, and it will usher in a boom in data business model. More and more businesses will use customer data to fuel personalized marketing, improved customer experience, and top-line growth. Consequently, ethical data ownership and privacy concerns will continue to be front-page issues as businesses walk the tightrope between consumer trust and compliance.
IoT Integrations and Edge Computing
The widespread use of IoT devices will lead to edge computing wherein the data will not be processed centrally. Rather than being cloud-based, analytics will be executed locally where data is being generated, leading to reduced latency and improved security. Smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation will be edge computing-based in order to facilitate real-time decision-making.
Uniting Nations Growth About Big Data and Ethics of Cybersecurity
Cybercrime is an international issue that needs to be addressed through global cooperation. So future laws will be based on cross-border cybersecurity systems, collaborative threat intelligence sharing, and cooperative law enforcement. Ethical controversies will revolve around averting cyber warfare, protecting vulnerable populations from cyber exploitation, and encouraging international cybersecurity norms.
The destiny of Big Data and cybersecurity ethics in the information era will be forged by emerging technologies, policy regimes, and evolving social values. While emerging technologies in AI, quantum computing, and IoT will open new pathways, data privacy, security, and equity issues will still take center stage. So organizations, governments, and citizens need to join hands to construct a secure yet ethically driven digital future.
Conclusion:
The intersection of big data and the ethics of cybersecurity brings opportunities and threats. While big data fuels superior decision-making and innovation, it raises issues about privacy, bias, and state surveillance as matters of ethics. Similarly, the threats to cybersecurity continuously evolve, and robust and ethical security mechanisms are needed to protect information. Organizational organizations are urged to adopt moral principles, follow compliance, and immerse themselves in good security practices in order to survive the challenges of big data ethically and securely.
With advancing technology, the trade between data-driven innovation and ethical cybersecurity will be a vital challenge. All stakeholders should work together in ensuring big data is used in a responsible manner while still protecting cybersecurity integrity. The future of cybersecurity ethics implications and robust security mechanisms to protect people’s rights and privacy.
Read more about Cyber Security from Technospheres.


