
Matrix of All Current Cybersecurity Issues
The one major concern to be seen within the current digital age is the concern of cybersecurity. The ever-moving pace of information technology coupled with an ever-increasing reliance on digital platforms has meant an individual, a business, or even a government has faced diverse cybersecurity threats. Thus, an ever-increasing need exists for understanding various forms of cybersecurity risks that can adversely affect data security, privacy, and the whole infrastructure. This paper shall be an extensive exploration of the matrix of all current issues related to cybersecurity, including types, causes, and possible solutions. In doing so, it will contribute to an increasingly greater understanding of the present state of cybersecurity and the challenges of protecting digital environments for organizations.
Introduction of Matrix of All Current Cybersecurity Issues
Cybersecurity in general refers to practices, tools, and policies created to prevent or protect computer systems, networks, and information from cyberattacks or unauthorized use/damage. Because of business operations and human interaction with computers every day, cybersecurity has taken center stage on the world scale. Experts identified all the range of cybersecurity problems that have then categorized them all to create a matrix of present issues in cybersecurity.
A matrix of all current cybersecurity issues refers to the framework from which various risks, vulnerabilities, and threats face categorization and evaluation in the cybersecurity landscape. This is a dynamic, ever-evolving framework as new technologies emerge and new threats to attack these technologies. This way, understanding the matrix of all current cybersecurity issues helps stakeholders better assess the risks before them so that they can realize and take the correct initiatives to mitigate them.
This article will dive into various cybersecurity issues, including malware, phishing, and even more advanced threats like artificial intelligence (AI) attacks and cloud security vulnerabilities. We’ll explore what causes these problems, how they affect us, and practical ways to tackle them.
Types of Cybersecurity Issues
There is no prominent type of issue in cybersecurity problems. Instead, there are the widest varieties possible that can damage an organization’s or individual’s digital security system. These consist of several broad categories, amongst which are, for example:
Malware:
Malware is the short term for “malicious software.” It ranks among the most common and destructive cybersecurity maladies. This includes viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware-all maliciously designed software with the aim to damage, steal or manipulate data on a computer system.
- Viruses and Worms: These are self-replicating programs that wander through networks that then infect other machines in its host, thus causing file destruction on an enormous scale. Systems may even be rendered unworkable in worst-case scenarios.
- Trojans: It takes the shape of software or files but bears malicious payloads within them. As soon as the Trojan self-executes, it provides the access to the attacker, and he continues with attacking the victim’s system.
- Ransomware: The ransomware malware encrypts files for a person and waits for the ransom payment before decrypting the files. The latest examples have demonstrated how catastrophic this could be for both individuals and organizations.
- Spyware is generally any kind of hidden or secret software that collects all information about the user’s activities on the system without prior knowledge or consent. It can exploit this information to take away sensitive data from your life, including login credentials, financial information, and much more.
- Malware is yet one of the growing threats. This has brought much attention, especially with the most recent ransomware attacks. Some reports have shown a 300 percent increase within the last five years itself, while they hold the first priority position in all current cybersecurity threats.
Phishing and Social Engineering

- Phishing and social engineering attacks essentially deceive humans into revealing information like a password or credit card number. Most phishing attacks rely on tricking unsuspecting people into believing that they are communicating with legitimate parties, such as the government, banks, or employers.
- Phishing: The attackers, using fraudulent email or message impersonating a trustworthy source, carry a link from a phishing website designed to get the personal data of the attacked user. An attack is extremely effective because of its nature attacking human trust instead of any weaknesses in the software.
- Spear Phishing: This is where phishing targets any individual or organizations. The cyber attacker can give a message intended to seem it is coming from a colleague or boss, boss, or your business partner – very convincing for sure.
- Vishing and Smishing: The attackers make use of voice calls (vishing) or short message service messages to hoodwink victims. Scammers often pose as customer service representatives or government officials, claiming they need you to provide some information over the phone or via text.
- The number one problem on the matrix of all existing cybersecurity issues is still phishing and social engineering attacks. Attackers have become incredibly sophisticated in their methods. In 2023, phishing attacks caused an estimated 80% of data breaches. Thus, this is the cause of its popularity in the threat landscape.
Data Breaches
- Data breaches mean that by unauthorized persons accessing in a way that violates confidentiality norms some sensitive information related to personal, financial, health, or other similar matters. Data breaches exert heavy tolls on their very victims and the institutions involved, inducing loss of identity, value destruction, loss of reputation, and all of this.
- Insider threats are those situations where existing or former employees release confidential information either by intent or mistake. Insider threats are very dangerous because the insider has usually gained access through some valid avenue, which makes the breach difficult to detect.
- Hacking:Hackers access information using techniques like SQL injection or brute-force attacks to target servers and databases. Once they gain access, they steal or manipulate the information, often to sell it on the dark web.
- An old software or system weakness exploitation is the fruit of a data breach. Cyber thieves usually target companies or organizations that haven’t implemented available security patches, as they exploit their systems and take advantage of known weaknesses.
- Data breaches continue to sweep huge organizations and government institutions off their feet. With a level of over 4 billion, the number of records exposed in data breaches worldwide attained a figure unacceptable for the year 2023. The problem has, in fact, become one of the issues that still remain in the matrix of such current issues in the field of cybersecurity.
The advanced persistent threat (APT)
- An Advanced Persistent Threat is an autonomous act where the determined threat actor executes a theft of sensitive information or causes long-term damage. Unlike the common cyberattacks, APTs are smart, stealthy, and executed for a longer period. In most scenarios, sophisticated, well-funded, and highly skilled attackers, like those from nation-states, carry out these attacks.
- APTs are usually multi-stage, which consists of reconnaissance, infiltration, data exfiltration, and maintaining access to the targeted victim’s network. Attackers design APTs to stay hidden for as long as possible, making them difficult to detect. Occasionally, an APT may be active for a period of months or even years since attackers gradually drain value data.
- Examples of APTs include the Stuxnet attack on Iran’s nuclear program and the SolarWinds attack that targeted several government agencies and private companies. These attacks are major focal points in the matrix of all current cybersecurity issues because of their complexity and severity.
Cloud Security Vulnerabilities
- New cyber challenges have resulted from rapid growth in cloud computing. While cloud service deliveries provide scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, they introduce new avenues with which cybercriminals can strike. Here are common issues with cloud security:
- Misconfigured Cloud Services: Wrong configuration of a cloud environment would expose sensitive information to people who should not see them. This mainly happens when firms fail to get access right or may have accidentally opened some resources up to the general public.
- Insecure APIs: The majority of the cloud-based applications use an API, which can become compromised if these are not in the right protection. Criminals can gain unauthorized access to cloud resources and data by exploiting weak or insecure APIs.
- Data Loss: A cloud service provider may not give proper protection to the data lost. Sometimes, infrastructure failures in cloud services, natural disasters, or human errors lead to the loss of partial data. Proper backup of data and good disaster recovery plans reduce the risks associated with such scenarios.
- One of the still pending problems that exists in the matrix of all existing cybersecurity problems is cloud security. More and more organizations are moving critical operations to the cloud. In the recent years, a few instances of misconfiguration and vulnerabilities have resulted in well-publicized breaches in cloud services, which becomes a huge worry for businesses regardless of size.
IoT Vulnerabilities
- But what’s exploding at an absolutely staggering rate is the Internet of Things. That naturally puts connected devices-the smart home appliances and the industrial machinery-at the top of the list. But as convenient and efficient as it all is, that networked gear puts up a huge cybersecurity risk.
- Weak Passwords: Many attackers can easily hack IoT devices because these devices are either simple or still use default passwords. They can exploit these vulnerabilities to take control of the devices, access sensitive information, and even use them as a gateway into larger networks.
- Lack of Encryption: Most IoT devices rarely use advanced encryption techniques to secure communication over networks. This means that hackers can easily map these communication streams and potentially access sensitive personal or confidential information.
- Insecure Firmware: Vulnerabilities in the underlying code allow an attacker to access the IoT devices. Regular updates and patches are crucial for securing these endpoints.
- As the devices connected increase by the day, IoT vulnerabilities make their way onto the list of all current security issues in cyberspace. According to some research, an estimated 75 billion IoT devices will be active by 2030, extending the attack surfaces for cyber thieves.
The Matrix of All Current Cybersecurity Issues
| Issue Type | Description | Common Threats | Mitigation Strategies |
| Malware | Malicious software designed to damage systems | Viruses, Trojans, Ransomware | Antivirus software, regular updates |
| Phishing and Social Engineering | Deceptive techniques to steal information | Phishing, Spear Phishing, Vishing | Employee training, email filtering |
| Data Breaches | Unauthorized access to sensitive data | Hacking, Insider Threats | Data encryption, access control, monitoring |
| Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) | Long-term, targeted cyberattacks | Nation-state actors, espionage | Continuous monitoring, threat intelligence |
| Cloud Security Vulnerabilities | Issues related to cloud-based systems | Misconfigurations, Data Loss | Cloud security policies, encryption |
| IoT Vulnerabilities | Security flaws in connected devices | Default passwords, unpatched firmware | configurations, regular updates |
Causes of Cybersecurity Issues
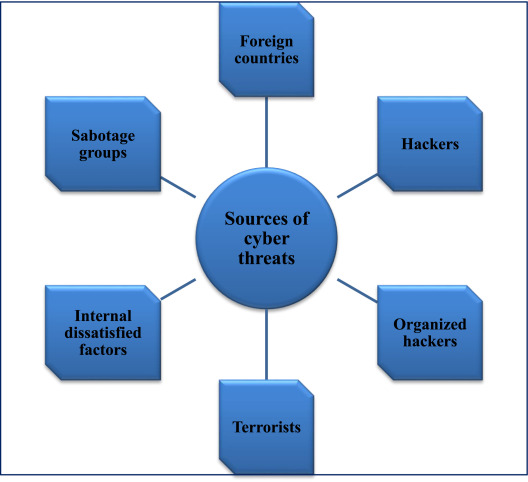
- A myriad of issues causes cybersecurity, including human faults, technological mishaps, and malicious intentions. Some of these primary causes are:
- Human Error: Human errors often lead to many cases of cybersecurity incidents because individuals might click an infected link, share a weak password, or even poorly configure the system. Even well-trained cybersecurity professionals may commit an error that may cause breaches or vulnerability.
- Software Vulnerabilities: Bugs or flaws in software codes make vulnerabilities that cyber-crooks can exploit. Attackers can identify these weaknesses and utilize them to obtain illegal access to systems and data.
- Lack of Awareness: Most people and organizations cannot value the value of cybersecurity, hence remain vulnerable to various attacks. Bad judgment and inappropriate behavior may arise from a lack of proper training and awareness.
- Advanced Threat Actors: Advanced or highly professional cybercrime organizations and nation-state attackers have more resources and capabilities to conduct highly targeted attacks. Sophisticated offenders use advanced techniques at times during the attack actions in order to evade detection for a long time and thereby cause damage.
Impacts of Cybersecurity Threats
- Cyber security threats could pose very serious, long-term consequences. Some of the most impactful ones include;
- Financial Losses: Cyber-attacks lead to direct financial losses, often appearing as fraud or extortion, and can involve the theft of sensitive financial information from companies or organizations. Take the 2020 Twitter hack, for instance, where attackers raided Bitcoin accounts, ultimately revealing a series of cleverly orchestrated social engineering attacks.
- Loss of reputation: It can lose the organizational reputation. The data breaches and cyberattacks may cover all forms of losses. It may result in loss of customers’ trust along with their trust among other business partners. In this situation, expected results can be sales declination, customers churn, and lost market share.
- Organizations can face fines and other penalties from regulatory authorities if they fail to take proper measures to protect sensitive data or comply with cybersecurity regulations. Huge amounts of fines may result from non-compliance with GDPR.
- Operational Disruption: Because of a cyberattack, operations may result in companies really stopping work with a great deal of lost time and productivity, and with some long-term damage to their resources. The 2017 NotPetya cyberattack falls into the latter category; a few major international companies became casualties, including Maersk and Merck.
Impact of Cybersecurity Issues on Organizations
| Impact Type | Description | Examples |
| Financial Losses | Direct monetary losses due to cyberattacks | Ransom payments, fraud, theft |
| Reputational Damage | Loss of public trust and consumer confidence | Brand damage, customer churn |
| Legal and Regulatory Consequences | Fines or legal action due to non-compliance | GDPR violations, lawsuits |
| Operational Disruption | Disruption of services, systems, and productivity | Downtime, loss of data, system failures |
Mitigation Strategies
- Risk mitigation strategies have been created within and outside the organization. They include some of the following:
- Staff Training: Employees will be told about the best practices in cybersecurity so that human error can be minimized and there will be better understanding of common threats. Such include recognizing phishing attempts, use of strong passwords, and observance of security protocols.
- MFA provides an extra layer of security in which users authenticate themselves with more than two methods, making it even more difficult for attackers to hack and gain unauthorized access, even if they have passwords.
- Software should be kept updated; make sure that any patches to the operating system and software are promptly made.
- Strategies on how organizations will respond in case of a cyberattack should have special plans whereby they can quickly detect the incident they can respond to it.
The conclusion:
The conclusion summarizes various aspects of the current cyberIEs, and gives a detailed picture of the diversifying, unrelentingly changeable threats that organizations and individuals across society will be faced with in the digital space. From simple ones like malware, phishing, or keyloggers to the more sophisticated APT or Internet of Things-related ones, the moving landscape of cybersecurity is characterized by a great deal of variety. As organizations begin to understand the full extent of these issues, along with their causes and effects, it becomes easier to take steps to mitigate them. As cybersecurity keeps its higher priority, it remains a case of good news providers that by adopting best practices, organizations and individuals will remain informed about emerging threats and act accordingly. The matrix of all current cybersecurity issues remains an effective tool in defense against all future attacks in the digital world.
Read more about Cyber Security from Technospheres.



The increasing reliance on digital platforms has made cybersecurity a critical concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Understanding the diverse threats and vulnerabilities in the cybersecurity landscape is essential for protecting data and infrastructure. The matrix of current cybersecurity issues provides a framework to categorize and evaluate these risks, helping stakeholders take proactive measures. As technology evolves, so do the threats, making it crucial to stay updated on the latest cybersecurity challenges.